Selection Guide
To find the right power generator, suitable welding unit, or the appropriate water pump, several factors should be considered. Below, you'll learn about what to consider during the selection process and what performance levels you can expect from various devices.
Selection Guide: Power Generators
1. How often and for what is the generator used?
"The question of how often the power generator is used should be quite easy to answer (once a year, daily, etc.). Since our power generators are very robust and reliable, they all withstand high usage frequencies. More interesting is the duration of operation with the power generator. For longer runtimes, attention should be given to an adequately large fuel tank. If you intend to use the unit for gardening, camping trips, or on a construction site in a residential area, sound pressure and possibly weight are important criteria. The noise limit currently stands at around 95 dB(A). If sensitive devices like laptops and TVs are to be powered, we recommend a generator with a Inverter generators, der Strom mit einer konstanten Frequenz produziert.
2. What performance is required?
| device/consumer | Performance | Koeffizient | Aggregat |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vibrating needle | 2.300 W | 2 | 4.600 W |
| Industrial vacuum cleaner | 1.800 W | 1,2 | 2.160 W |
| Concrete machine | 850 W | 3,5 | 2.975 W |
| Compressor | 3.000 W | 2 | 6.000 W |
| Crepe hot plate | 4.000 W | 1,2 | 4.800 W |
| Gypsum spraying machine | 4.300 W | 3,5 | 15.050 W |
| Mixer | 3.500 W | 2 | 7.000 W |
| Grinding machine | 2.200 W | 1,2 | 2.640 W |
| Refrigerator | 200 W | 3,5 | 700 W |
| Cooling display case | 1.500 W | 3,5 | 5.250 W |
| Freight elevator | 2.800 W | 2 | 5.600 W |
| Neon Lampe | 500 W | 3,5 | 1.750 W |
| High-pressure cleaner | 2.500 W | 3,5 | 8.750 W |
| Drill machine | 800 W | 1,2 | 960 W |
| Stove burne | 6.000 W | 1 | 6.000 W |
| Oil heater | 500 W | 1,2 | 600 W |
| Belt sander | 1.000 W | 1,2 | 1.200 W |
| Planer | 800 W | 1,2 | 960 W |
| Slot cutter | 2.000 W | 1,2 | 2.400 W |
| circular saw | 1.100 W | 1,2 | 1.320 W |
3. Example
You want to operate a 2,300 W rotary hammer with your power generator. Therefore, take the coefficient for a drilling machine and multiply it by the power: 2,300 W x 1.2 = 2,760 W.
That means you would require a 2,800 W power generator. Assuming you work 8 hours a day in a residential area, the sound pressure should be low, and the tank capacity should suffice. The SDMO Alize 3000 would be a recommended choice in this scenario.
Selection aid: welding units
1. What is important and how often is the welding unit used?
Welding units are used for welding and maintenance tasks. The models we offer are easy to transport and can also be used as emergency power generators. For welding – regardless of the electrode used – we recommend using direct current. For heavy usage, consider opting for an efficient diesel welding unit. These provide a longer runtime compared to similar gasoline welding units, which are more suitable for occasional use.
2. Welcher Elektroden-Typ wird benutzt?
Our welding units support all types of electrodes. From the common rutile electrode to the cellulose electrode for fillet welding, to the basic-coated continuous welding current electrode for highly technical and completely secure connections.
Selection guide: water pumps
1. Which liquids should be pumped?
We offer you two different water pump product lines. The Aqualine "INTENS" is suitable for water. This line is divided into the ST pumps for clear or slightly polluted water, and the TR pumps for silt and mud. On the other hand, the water pumps of the Aqualine "SPECIALIST" are designed for special applications. With these pumps, chemicals, liquid fertilizers, saltwater, or liquids with solid particles up to 30 mm in size can be pumped, for example.
2. What pump head is required?
The pump head depends on the type of installation and application (water drainage, irrigation, etc.). It is determined by adding the suction head (vertical distance between water level and pump axis), the discharge head (vertical distance between pump axis and water outlet), and pressure drop (typically 20%, depending on pipeline quality, accessories, etc.), as illustrated in the following diagram:
Water network example for determining the pump height:
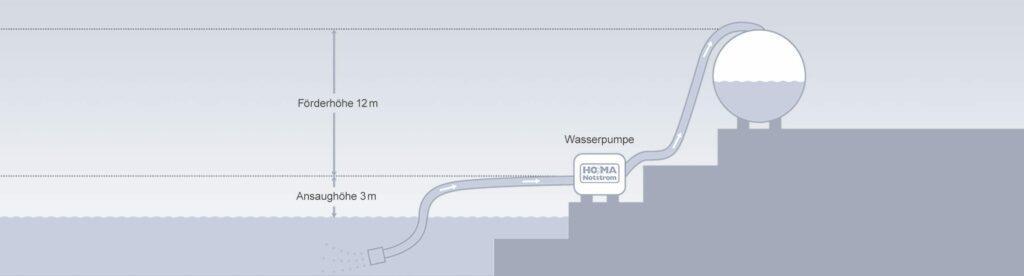

pressure drop (ca. 20%) = (3 m + 12 m) * 0,2 = 3
Network pumping height = 3 m + 12 m + 3 = 18 m
3. What flow rate and how much pressure is required?
The flow rate is the maximum amount of water that the pump can deliver. This rate decreases based on the required pump head. For every water pump in our shop, you will find a corresponding performance curve. Using this curve, you can read the flow rate that the water pump achieves at the corresponding pump head. Additionally, you can divide the calculated pump head by 10 to obtain the pressure in bars. If this pressure is not sufficient, a more powerful pump is recommended.
protection classes
Our products have information on different protection classes. The International Protection (IP) number is regulated according to the DIN standard 40050 and consists of two digits. The first digit defines the protection against contact and foreign bodies, the second digit the water and moisture protection. The following IP numbers can be found in our shop:
- IP 20: protection against foreign bodies (> 12 mm). No protection against water.
- IP 23: Protection against foreign objects (> 12 mm) and light rain (90-60°).
- IP 40: protection against foreign objects (> 1 mm). No protection against water.
- IP 44: protection against foreign objects (> 1 mm) and splashing water from all directions.
- IP 54: protection against dust and splash water from all directions.
- IP 68: Completely dustproof and protection against permanent immersion.





